“… our users depend on excel, they love excel because it gives them flexibility to create their own pivot tables, interact with data as they wish and find answers to their questions and I don’t want a Power BI Report. Can you make it happen? “- One of our beloved customers.
Absolutely, enters the semantic model, first the definition.
Semantic model is a conceptual framework that represents the meaning and relationship between entities, concepts and data in an application. It provides an easier way of understanding and organizing information.
The key components of semantic model include
- Entities – things that exist in data domain (people, products, places, events or processes).
- Relationships – Connection and association between entities.
- Attributes – Properties and characteristics that describe entities and their relationships.
- Hierarchies – Vertical arrangement of attributes that are related, with entities being subordinates of each other except the topmost one.
- Taxonomies – Entities classifications based on their shared characteristics
Sounds familiar? That’s because many data representations are now following sematic model for ease of use while empowering business users to consume and interpret organizational data to meet their needs. This leads to data democratization which leads to data-driven organizations.
Use cases for Sematic Model includes
- Data modeling: Designing and organizing data in a way that reflects the underlying meaning, improving data management and integration.
- Natural language processing: Helping applications understand the meaning and context of human language by leveraging semantic models.
- Knowledge representation: Capturing the meaning and relationships of information in a structured way, enabling better understanding and reasoning.
- Ontology engineering: Creating formal representations of knowledge domains, enabling semantic-based information retrieval and reasoning.
- Linked data and the Semantic Web: Enabling the interconnection and meaningful exchange of data across different systems and platforms.
While the concept of a semantic model appears straightforward, its implementation within an organization can present significant challenges. They include
- Data accessibility
- Lack of appropriate tools
- Insufficient user skills
Some of the tools in the market that can help solve these issues include
- Power BI
- Excel
- Gen AI
Microsoft Fabric Power BI Semantic Model
In Microsoft Fabric, Power BI semantic models are a logical data description of an analytical domain, with metrics, calculations, hierarchies, business friendly terminology, and representation, to enable deeper analysis. Typically structured as a star schema with facts and dimensions that allow analysis, filtering, slicing and dicing of the data, to drill downs and comprehensive calculations.
Microsoft fabric can generate a semantic model for lakehouse, or warehouse and it can also be inherited from parent objects. With sematic model in place, Power BI visualization can be built in the web or using Power BI Desktop.
Key features of the Power BI semantic model include:
- Ability to establish relationships between tables, descriptions, and hierarchies.
- Ability to create measures and standardized metrics for repeatable analysis.
- Defining data types and categories for columns.
- Enhancing security with row-level security.
- Supporting data consumption from Power BI, Excel, and Tableau.
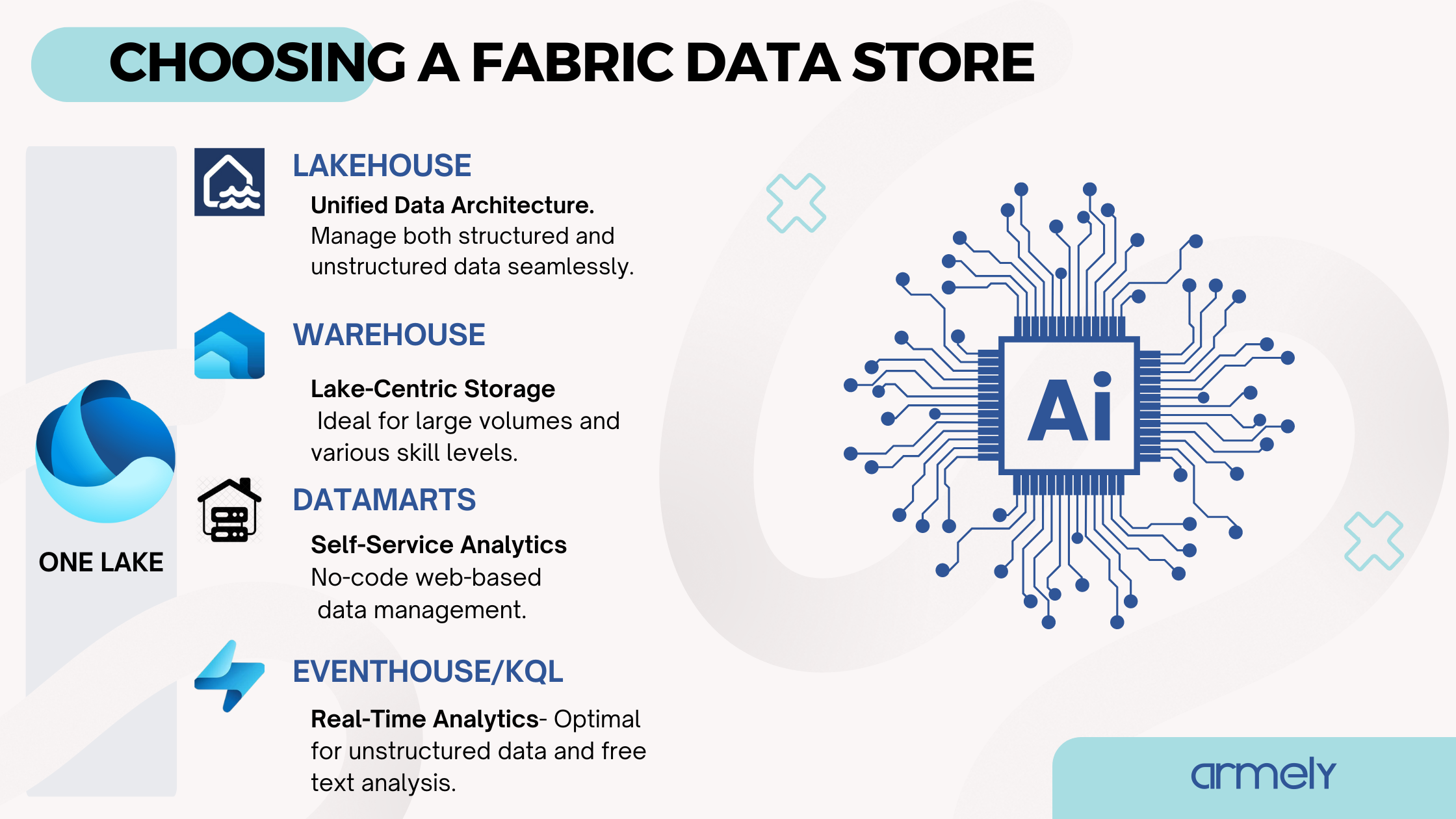
Data Lake Mode
A new method of analyzing large datasets in Power BI. It uses Parquet files from a data lake without having to query a Warehouse or SQL endpoints. This method is faster than traditional DirectQuery or Import modes, as it bypasses the need for query execution or memory-based data refreshes. It also avoids data duplication into the model.
Practical use of a semantic model
From Excel you can easily connect to a Power BI dataset by navigating to Power Platform à Power BI, after this selection they are presented with Power BI Datasets that allow them to build their own excel reports to get then answers their questions.
Copilot for Power BI
Copilot for Power BI is a feature that integrates Generative AI (Gen AI) technology into the Microsoft Power BI platform, aiming to enhance the data analysis and reporting capabilities of Power BI users. Some of the features in Copilot that are a result of a solid semantic model include
- Natural Language Interaction:
- Allows users to interact with Power BI using natural language, such as asking questions or providing prompts.
- The Gen AI-powered Copilot understands the user's intent and translates the natural language input into the appropriate Power BI actions and visualizations.
- Automated Insights and Recommendations:
- Analyzes the data in the Power BI report and proactively provides insights, recommendations, and suggested actions to the user.
- This includes highlighting key trends, outliers, or anomalies in the data, as well as suggesting relevant visualizations or report layouts.
- Conversational Analytics:
- Users can engage in a conversational dialogue with Copilot, asking follow-up questions, refining their queries, or exploring the data further.
- Copilot responds in natural language, providing explanations, interpretations, and additional insights based on the user's interactions.
- Automated Report Generation:
- Generates complete Power BI reports based on natural language prompts or specific data analysis requirements.
- This includes selecting appropriate data sources, designing visualizations, and structuring the report layout.
- Code Generation and Automation:
- Copilot can assist users in writing custom Power BI queries, measures, and DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) code.
- It can generate code snippets, provide explanations, and suggest optimizations based on the user's input and the underlying data model.
- Collaboration and Sharing:
- Enables collaborative experiences, where users can share their insights, reports, and questions with others, and the Gen AI-powered Copilot can respond and engage in discussions.
- This facilitates knowledge-sharing and decision-making within an organization.
Overall, the integration of organization data to semantic models holds significant potential to enhance the creation, expansion, interaction, maintenance, and validation of these knowledge representation systems. However, it also raises important considerations around transparency, interpretability, and the potential for bias and errors. Careful design, testing, and governance are essential to ensure the responsible and ethical development and deployment of these integrated systems.