Choosing a Fabric Data Store
OneLake, Warehouse, Lakehouse, Datamart, and Eventhouse are the main data storage solutions in Microsoft Fabric. In this article, we will take a deep dive into defining each of these storage solutions, examining their unique features. This guide will help you make the right decision on where to store your data while moving to Microsoft Fabric.
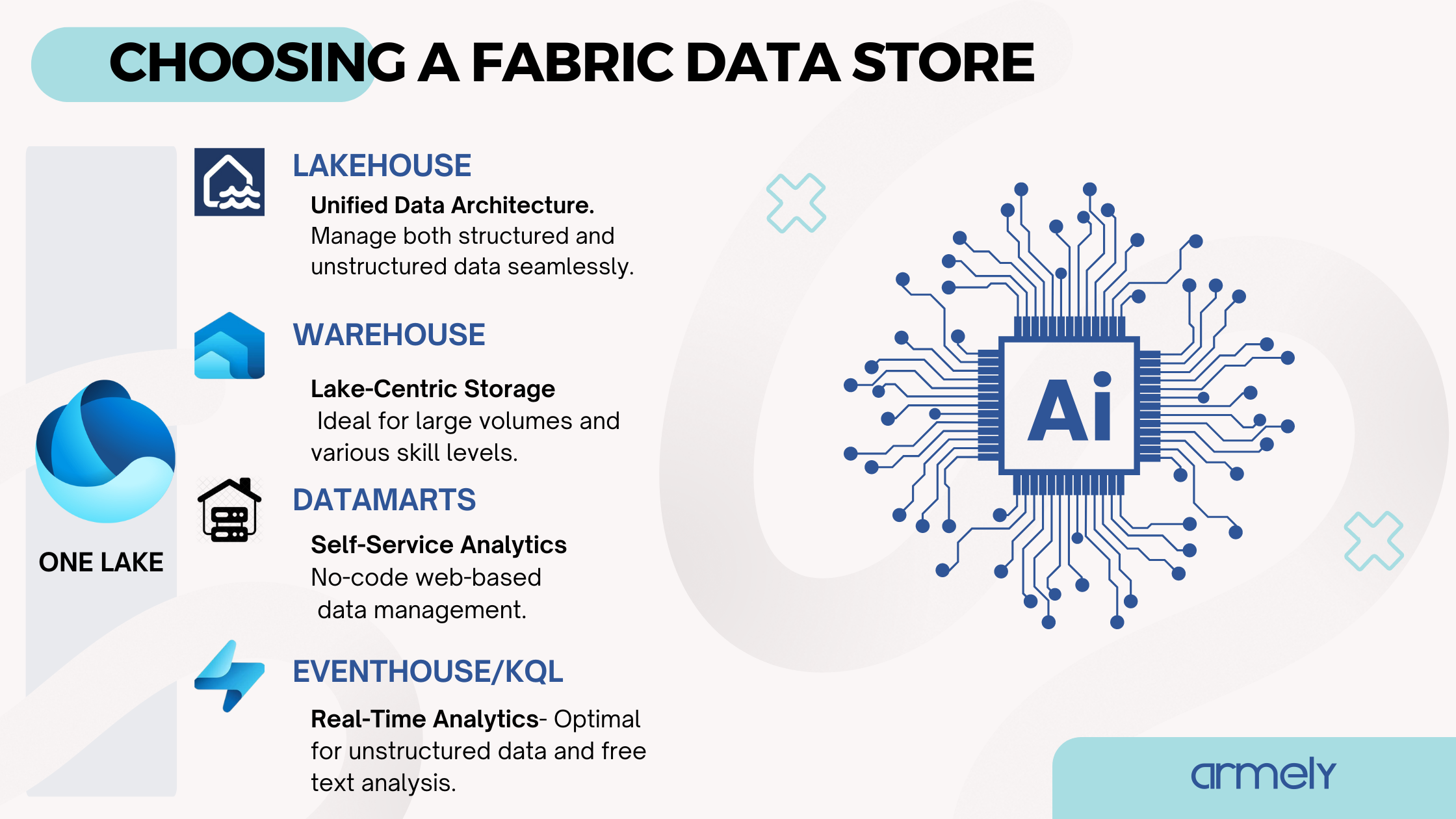
OneLake
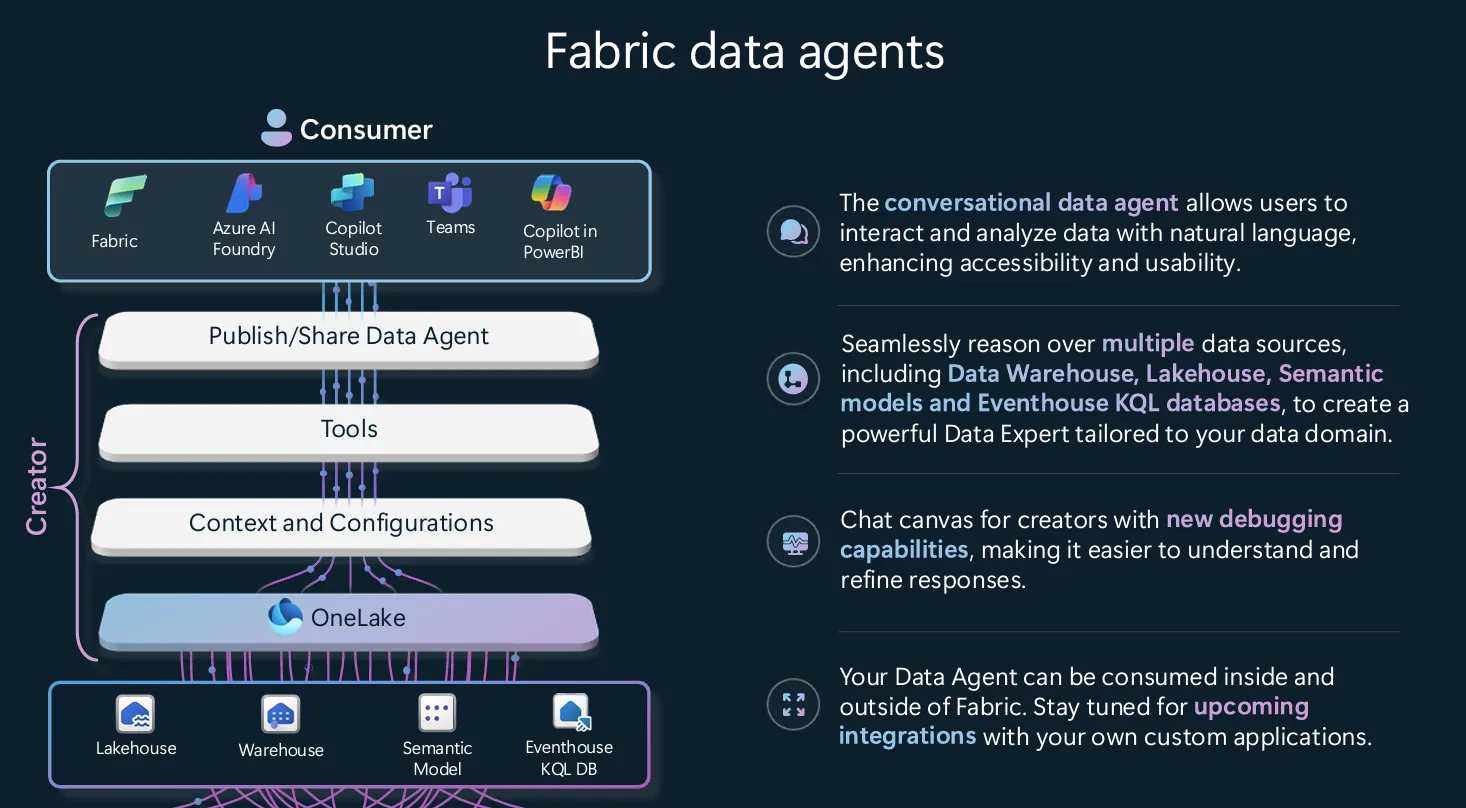
OneLake is a single, unified, logical data lake for your whole organization. It’s the OneDrive for data. OneLake comes automatically with every Microsoft Fabric tenant and is designed to be the single place for all your analytics data.
Warehouse
A lake-centric data warehouse built for any skill level (Citizen developer, DBA to Data Engineer) allowing a centralized repository that can handle very large volumes of data as a SaaS environment.
Data is ingested into warehouse though pipelines dataflows, Cross database Querying or COPY INTO commands. Once ingested, it can be analyzed by different groups though sharing or databases querying.
Lakehouse
A lakehouse is a data architecture platform that allows storage, management and analysis of both structured and unstructured data in Microsoft Fabric. Lakehouse, like warehouse, has the capacity to handle a very large volume of data.
Data is ingested into lakehouse via File upload from local computer (automatically determines the file structure and generates metadata for it), Pipelines, dataflows and Spark libraries in notebook. Lakehouse also has the capability to set up shortcuts that allows users to reference data without having to copy or create a separate copy.
Lakehouse allows data streaming which is a continuous data ingesting as the data becomes available.
Datamarts
Datamarts are self-service analytics solution that enables users to explore data loaded in a managed database in a web-based environment.
Being a web-based solution, Datamarts are simple and require no-code experience to ingest data. Data is ingested from different sources, can be cleansed using an ETL process in Power Query then thereafter loaded into a fully managed Azure SQL database.
Eventhouse/KQL
Eventhouse is a solution designed to handle and analyze large volumes of data particularly when near real-time analytics and exploratory is a requirement. They are the preferable engine for handling unstructured and semi structured data like free text analysis. It’s also designed as a workspace of databases allowing it to be sharable across projects and managed all at once.
Data is ingested into KQL database as the data store.
Now that we have some understanding of the storage elements in Fabric, here is the side-by-side comparison of these data stores
|
|
Warehouse |
Lakehouse |
Datamart |
Eventhouse KQL Database |
|
Data volume |
Unlimited |
Unlimited |
Up to 100 GB |
Unlimited |
|
Type of data |
Structured |
Unstructured,semi-structured,structured |
Structured |
Unstructured, semi-structured, structured |
|
Primary developer persona |
Data warehouse developer, SQL engineer |
Data engineer, data scientist |
Citizen developer |
Citizen Data scientist, Data engineer, Data scientist, SQL engineer |
|
Primary developer skill set |
SQL |
Spark(Scala, PySpark, Spark SQL, R) |
No code, SQL |
No code, KQL, SQL |
|
Data organized by |
Databases, schemas, and tables |
Folders and files, databases, and tables |
Database, tables, queries |
Databases, schemas, and tables |
|
Read operations |
Spark,T-SQL |
Spark,T-SQL |
Spark, T-SQL, Power BI |
KQL, T-SQL, Spark, Power BI |
|
Write operations |
T-SQL |
Spark(Scala, PySpark, Spark SQL, R) |
Dataflows, T-SQL |
KQL, Spark, connector ecosystem |
|
Multi-table transactions |
Yes |
No |
No |
Yes, for multi-table ingestion. See update policy. |
|
Primary development interface |
SQL scripts |
Spark notebooks,Spark job definitions |
Power BI |
KQL Queryset, KQL Database |
|
Security |
Object level (table, view, function, stored procedure, etc.), column level, row level, DDL/DML, dynamic data masking |
Row level, table level (when using T-SQL), none for Spark |
Built-in RLS editor |
Row-level Security |
|
Access data via shortcuts |
Yes (indirectly through the lakehouse) |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
Can be a source for shortcuts |
Yes (tables) |
Yes (files and tables) |
No |
Yes |
|
Query across items |
Yes, query across lakehouse and warehouse tables |
Yes, query across lakehouse and warehouse tables;query across lakehouses (including shortcuts using Spark) |
No |
Yes, query across KQL Databases, lakehouses, and warehouses with shortcuts |
|
Advanced analytics |
|
|
|
Time Series native elements, Full geospatial storing and query capabilities |
|
Advanced formatting support |
|
|
|
Full indexing for free text and semi-structured data like JSON |
|
Ingestion latency |
|
|
|
Queued ingestion, Streaming ingestion has a couple of seconds latency |